Ap chem unit 9 progress check frq – Embark on an enlightening journey with the AP Chemistry Unit 9 Progress Check FRQ, a comprehensive assessment designed to evaluate your understanding of equilibrium and electrochemistry. Prepare to unravel the intricate dynamics of chemical reactions, quantify equilibrium concentrations, delve into acid-base equilibria, explore solubility and complex ion equilibria, and unravel the mysteries of electrochemistry.
This guide provides a roadmap to success, offering a clear overview of key concepts, expert insights, and practical problem-solving strategies. Whether you’re a seasoned AP Chemistry student or an aspiring chemist, this resource will empower you to conquer the challenges of the FRQ and excel in your studies.
Chemical Equilibrium: Ap Chem Unit 9 Progress Check Frq
Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic state in which the forward and reverse reactions of a chemical reaction occur at the same rate, resulting in no net change in the concentrations of the reactants and products. This equilibrium is a result of the constant collision of particles and the exchange of energy between them.
Factors Affecting Equilibrium Position (Le Chatelier’s Principle)
The position of equilibrium can be shifted by changing the conditions of the reaction. According to Le Chatelier’s principle, if a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system will shift in a direction that relieves the stress.
- Concentration:Increasing the concentration of reactants shifts the equilibrium to the product side, while increasing the concentration of products shifts the equilibrium to the reactant side.
- Temperature:Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the side of the reaction that absorbs heat (endothermic reaction), while decreasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the side that releases heat (exothermic reaction).
- Volume (for gas reactions):Increasing the volume of the reaction vessel shifts the equilibrium to the side with more moles of gas, while decreasing the volume shifts the equilibrium to the side with fewer moles of gas.
- Pressure (for gas reactions):Increasing the pressure shifts the equilibrium to the side with fewer moles of gas, while decreasing the pressure shifts the equilibrium to the side with more moles of gas.
Examples of Equilibrium Shifts, Ap chem unit 9 progress check frq
- Haber process:The production of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen is an exothermic reaction. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the reactant side, decreasing the yield of ammonia.
- Water-gas shift reaction:The conversion of carbon monoxide and water to hydrogen and carbon dioxide is an endothermic reaction. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the product side, increasing the yield of hydrogen.
- Limestone decomposition:The decomposition of limestone to form calcium oxide and carbon dioxide is an endothermic reaction. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the product side, increasing the yield of calcium oxide.
Equilibrium Calculations
Equilibrium constants (Kc and Kp) are used to quantify the extent to which a reaction proceeds to completion. Kc is the equilibrium constant expressed in terms of molar concentrations, while Kp is the equilibrium constant expressed in terms of partial pressures.
The equilibrium concentrations of reactants and products can be calculated from the initial concentrations and the equilibrium constant using the following equations:
- For Kc:[A]eq = [A]i – [C]eq, [B]eq = [B]i – [C]eq, [C]eq = [C]
- For Kp:P[A]eq = P[A]i – P[C]eq, P[B]eq = P[B]i – P[C]eq, P[C]eq = P[C]
where [A]i, [B]i, and [C]i are the initial concentrations of reactants and products, and [A]eq, [B]eq, and [C]eq are the equilibrium concentrations.
ICE tables (Initial, Change, Equilibrium) are a convenient way to solve equilibrium problems. In an ICE table, the initial concentrations, the changes in concentrations, and the equilibrium concentrations are listed in a tabular format.
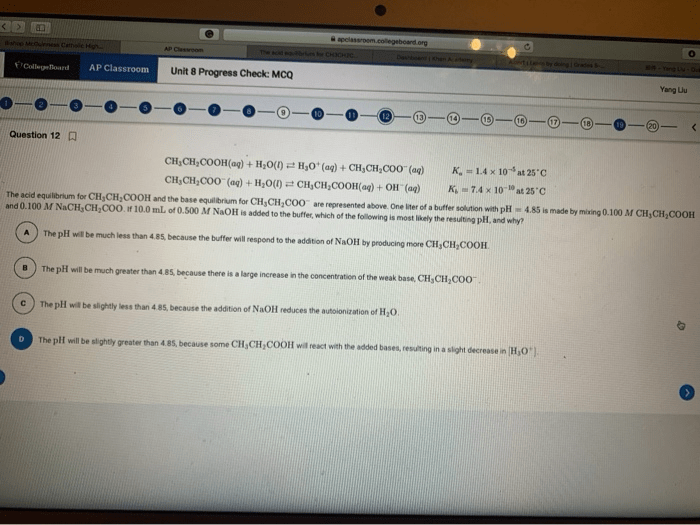
Acid-Base Equilibria
Acid-base reactions are chemical reactions that involve the transfer of protons (H+ ions). The strength of an acid or base is determined by its ability to donate or accept protons.
The pKa value of an acid is a measure of its acidity. The lower the pKa value, the stronger the acid. The pKb value of a base is a measure of its basicity. The lower the pKb value, the stronger the base.
Acid-base titrations are used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base. The equivalence point of a titration is the point at which the moles of acid and base are equal.
Solubility Equilibria
Solubility is the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent. The solubility product (Ksp) is a constant that expresses the equilibrium between a solid solute and its ions in solution.
The solubility of an ionic compound can be calculated from its Ksp using the following equation:
- [A+][B-] = Ksp
where [A+] and [B-] are the equilibrium concentrations of the ions.
The solubility of an ionic compound can be affected by factors such as temperature and the common ion effect.
Complex Ion Equilibria
Complex ions are formed when a metal ion combines with a ligand. The formation constant (Kf) is a constant that expresses the equilibrium between a metal ion and a ligand to form a complex ion.
The formation of complex ions can be used to control the solubility of metal ions and to separate different metal ions from each other.
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the study of the relationship between electrical energy and chemical reactions. Electrochemical cells are devices that use chemical reactions to generate electricity or use electricity to drive chemical reactions.
The cell potential (E) of an electrochemical cell is a measure of the driving force of the reaction. The cell potential is related to the free energy change (ΔG) of the reaction by the following equation:
- ΔG = -nFE
where n is the number of electrons transferred in the reaction and F is the Faraday constant.
Electrochemical cells have a wide range of applications, including batteries, fuel cells, and sensors.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the significance of equilibrium constants (Kc and Kp)?
Equilibrium constants are quantitative measures of the extent to which a reaction proceeds towards completion. They provide valuable insights into the favourability and direction of reactions, enabling us to predict the composition of reaction mixtures at equilibrium.
How can I effectively solve acid-base titration problems?
To solve acid-base titration problems accurately, a systematic approach is crucial. Begin by identifying the equivalence point, where the moles of acid and base are equal. Utilize titration curves to determine the pH at various points during the titration and employ stoichiometry to calculate unknown concentrations.
What is the role of temperature in solubility equilibria?
Temperature plays a significant role in solubility equilibria. In general, the solubility of solids increases with increasing temperature, while the solubility of gases decreases. This behaviour can be explained by considering the opposing effects of temperature on the dissolution process and the equilibrium position.