Translate the medical term myelomeningocele as literally as possible. – Translate the medical term “myelomeningocele” as literally as possible, and a fascinating story unfolds, revealing the intricate connection between etymology and anatomy. Join us on a journey to decipher this complex term, unraveling its literal meaning and exploring its profound implications in the medical realm.
Delving into the etymology of “myelomeningocele,” we embark on a linguistic adventure that unveils the origins and significance of its individual components. “Myelo” originates from the Greek word “myelos,” meaning “marrow,” alluding to the spinal cord’s location within the vertebral canal.
“Meningo” stems from the Greek word “meninx,” referring to the meninges, the protective membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. Lastly, “cele” originates from the Greek word “κήλη” (kēlē), meaning “tumor” or “swelling,” aptly describing the characteristic protrusion associated with myelomeningocele.
Etymology of Myelomeningocele
The term “myelomeningocele” is derived from Greek and Latin roots and literally means “spinal cord membrane hernia.”
“Myelo”refers to the spinal cord, which is the central nervous system structure enclosed within the spinal canal.
“Meningo”refers to the meninges, which are the protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord.
“Cele”is a Latin term meaning “hernia” or “protrusion.” It describes the abnormal protrusion of the spinal cord and meninges through a defect in the vertebral column.
Anatomical Location of Myelomeningocele
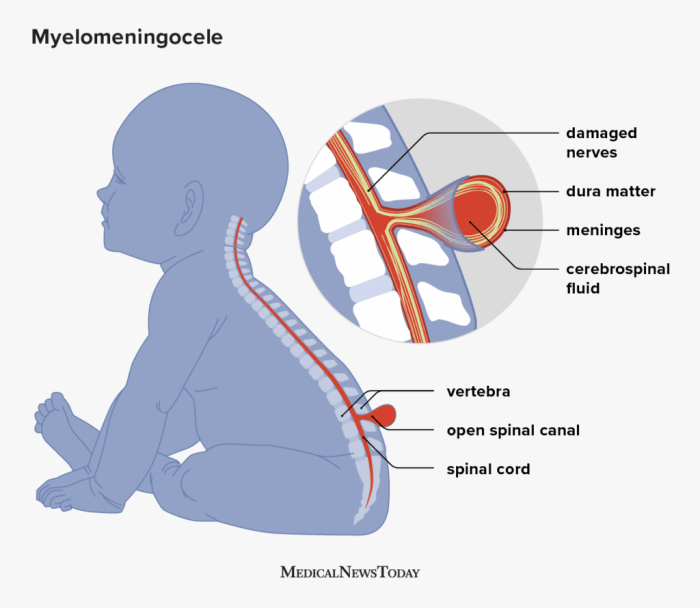
The spinal cord is located within the spinal canal, which is formed by the vertebrae of the spine. The meninges are composed of three layers: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. These layers protect the spinal cord from injury and infection.
Myelomeningocele arises during embryonic development when the neural tube fails to close properly. The neural tube is the precursor to the brain and spinal cord. When the neural tube fails to close at the caudal end, it results in a myelomeningocele.
Pathophysiology of Myelomeningocele
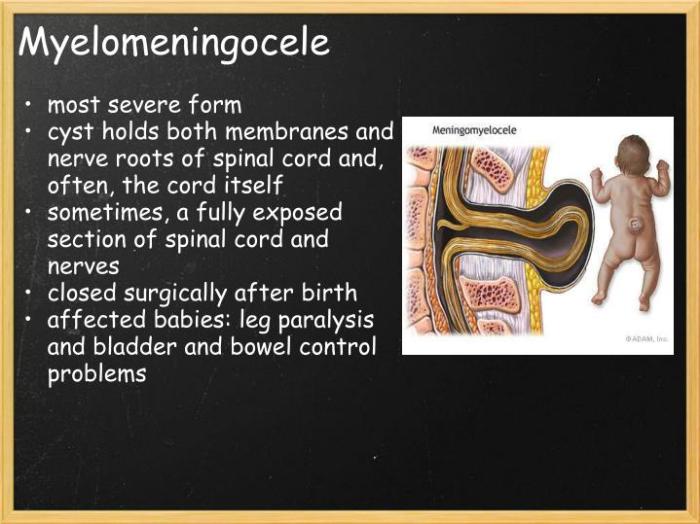
Myelomeningocele is a developmental defect that occurs when the neural tube fails to close properly during pregnancy. This results in a protrusion of the spinal cord and meninges through a defect in the vertebral column.
The protrusion can vary in size and location, and it can affect the function of the spinal cord and nerves. Myelomeningocele can also lead to other complications, such as hydrocephalus, which is an accumulation of fluid in the brain.
The long-term effects of myelomeningocele on neurological function can vary depending on the severity of the defect. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms, while others may have more severe disabilities.
Treatment Options for Myelomeningocele
The primary treatment for myelomeningocele is surgical repair. Surgery is typically performed within the first few days of life to close the defect in the vertebral column and protect the spinal cord and nerves.
The timing and techniques of surgical repair vary depending on the severity of the defect. In some cases, the surgery may be performed in utero.
The potential outcomes and complications of surgical intervention for myelomeningocele include infection, nerve damage, and cerebrospinal fluid leakage.
Clinical Manifestations of Myelomeningocele
| Physical Findings | Neurological Findings |
|---|---|
| Spinal defect | Paralysis or weakness in the legs |
| Hydrocephalus | Sensory loss in the legs |
| Clubfoot | Bowel and bladder incontinence |
| Hip dislocation | Cognitive impairment |
Early diagnosis and intervention are essential for improving outcomes in individuals with myelomeningocele. Multidisciplinary care is required to address the medical, surgical, and developmental needs of these individuals.
Differential Diagnosis of Myelomeningocele: Translate The Medical Term Myelomeningocele As Literally As Possible.
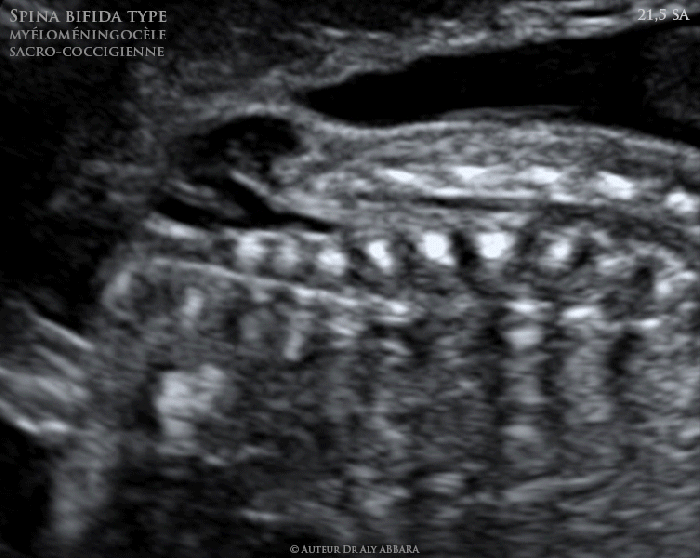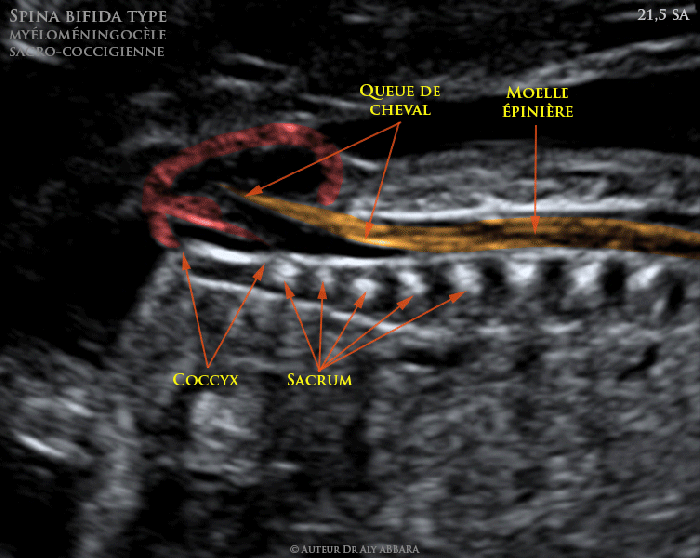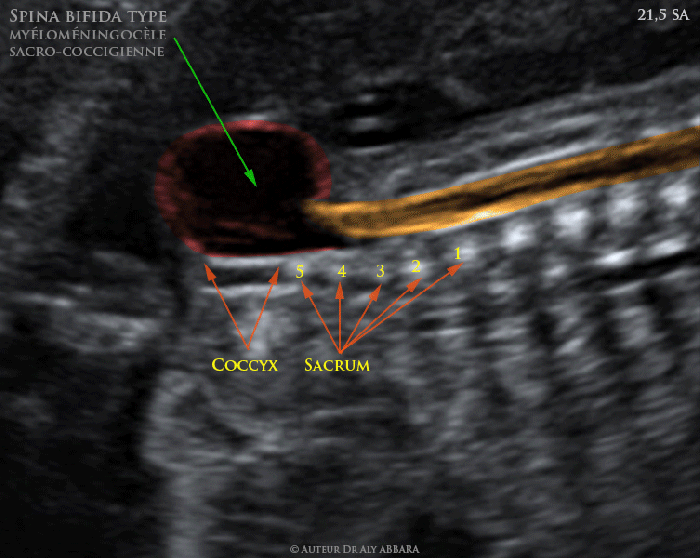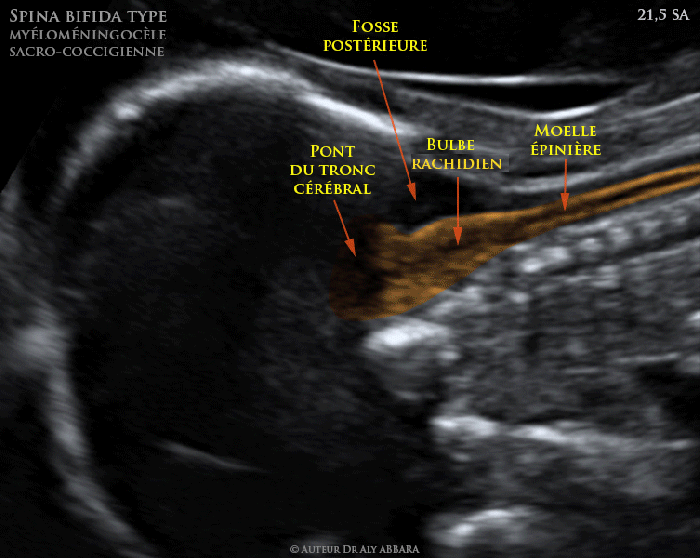
Other conditions that can mimic the symptoms of myelomeningocele include:
- Spina bifida occulta
- Meningocele
- Lipomeningocele
- Teratoma
Accurate diagnosis is important to guide appropriate treatment. Imaging studies, such as ultrasound and MRI, can help to differentiate myelomeningocele from other conditions.
Epidemiology of Myelomeningocele
Myelomeningocele is a relatively rare condition, affecting approximately 1 in 1,000 live births. The incidence is higher in certain populations, such as those of Hispanic and Asian descent.
The risk factors for myelomeningocele include:
- Family history of the condition
- Maternal use of certain medications, such as valproic acid
- Maternal obesity
- Diabetes
Understanding the epidemiology of myelomeningocele is important for prevention and management. Public health measures, such as folic acid fortification and genetic counseling, can help to reduce the incidence of the condition.
Q&A
What is the literal meaning of “myelomeningocele”?
Myelomeningocele literally translates to “marrow membrane swelling,” accurately describing the protrusion of the spinal cord and meninges through an opening in the spinal column.
What is the significance of understanding the etymology of medical terms?
Understanding the etymology of medical terms provides valuable insights into their historical origins, anatomical relationships, and clinical significance, enhancing our comprehension of complex medical concepts.
How does myelomeningocele arise during embryonic development?
Myelomeningocele occurs when the neural tube fails to close properly during the early stages of embryonic development, resulting in the protrusion of the spinal cord and meninges through the opening in the spinal column.