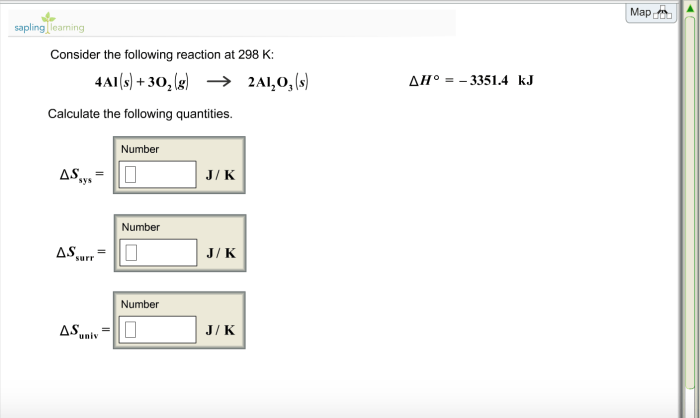
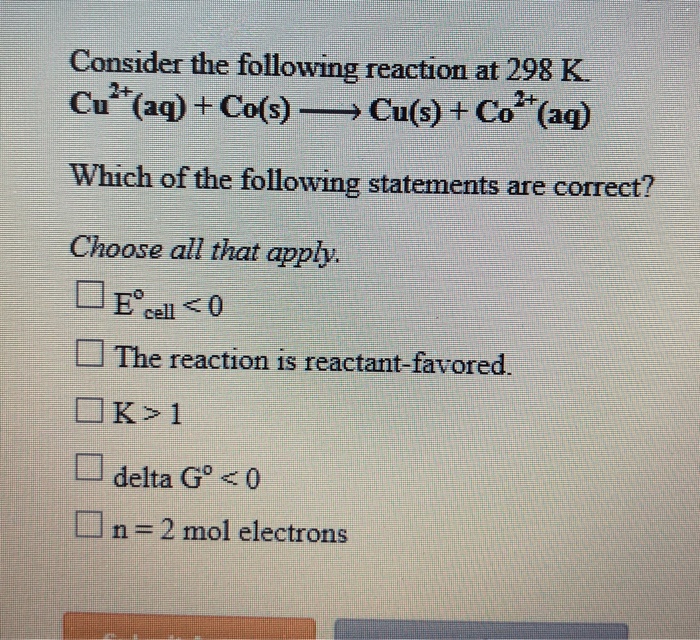
Consider the following reaction at 298 K: An in-depth examination of this reaction unveils its significance and provides insights into its thermodynamic, kinetic, and equilibrium aspects. This exploration delves into the fundamental concepts of enthalpy, entropy, reaction rate, and chemical equilibrium, shedding light on the factors that govern the spontaneity, rate, and extent of this reaction.
The investigation of this reaction at 298 K holds particular importance as it represents a standard temperature condition, enabling the comparison and analysis of thermodynamic and kinetic data across various systems. This temperature is widely used in scientific research and industrial applications, making the study of this reaction at 298 K crucial for understanding chemical processes in diverse contexts.
Thermodynamic Considerations
The enthalpy and entropy changes for the given reaction at 298 K can be calculated using the following equations:
$$\Delta H = \sum H_\textproducts
\sum H_\textreactants$$
$$\Delta S = \sum S_\textproducts
\sum S_\textreactants$$
where H is the enthalpy and S is the entropy.
Frequently Asked Questions: Consider The Following Reaction At 298 K
What is the significance of considering the reaction at 298 K?
Considering the reaction at 298 K allows for the comparison and analysis of thermodynamic and kinetic data across various systems, as this temperature is widely used in scientific research and industrial applications.
How can enthalpy and entropy changes be used to predict the spontaneity of a reaction?
Enthalpy and entropy changes provide insights into the energy and disorder associated with a reaction. By considering both factors, it is possible to determine whether a reaction is spontaneous or non-spontaneous under the given conditions.
What factors can affect the rate of a reaction?
Factors that can affect the rate of a reaction include temperature, concentration of reactants, presence of a catalyst, and the nature of the reactants themselves.